The Emerald Elixir: A Journey Through the Full Spectrum of Green Tea’s Benefits
In the quiet reverence of ancient rituals and the bustling laboratories of modern science, a humble leaf has transcended its origins to become a celebrated symbol of wellness. Green tea, the unoxidized progeny of the Camellia sinensis plant, carries within its emerald embrace a legacy of health that spans millennia. From the serene tea ceremonies of the East to the sophisticated clinical trials of the West, its story is one of profound discovery – a narrative woven through the intricate tapestry of human biology, promising benefits that touch every corner of our being, from the first line of defense in our mouths to the deepest recesses of cellular protection against formidable adversaries like cancer.
This is not merely a beverage; it is an elixir, a testament to nature’s subtle power. Join us on a journey through the full spectrum of green tea’s benefits, unraveling the science behind its ancient wisdom and discovering how this emerald potion can fortify our health, one sip at a time.
Chapter 1: The Alchemy of the Leaf – Unveiling Green Tea’s Bioactive Symphony
The distinction of green tea, and indeed the genesis of its remarkable health profile, lies in its unique processing. Unlike black tea, which undergoes significant oxidation, green tea leaves are swiftly steamed or pan-fired after harvest. This crucial step inactivates the enzymes responsible for oxidation, preserving the leaf’s vibrant green hue and, more importantly, its delicate yet potent treasure trove of polyphenols, particularly catechins. This careful alchemy ensures that the leaf’s inherent vitality is captured, ready to be infused into water.
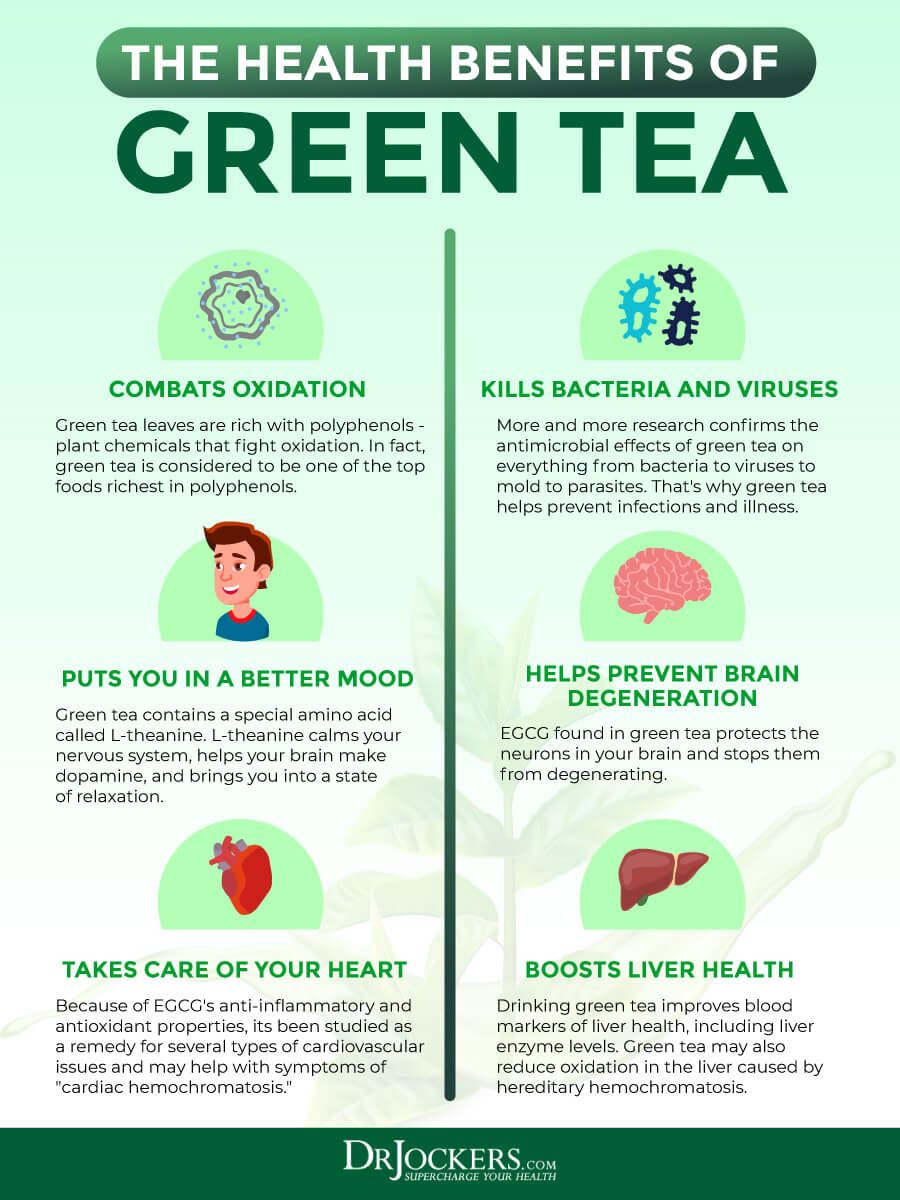
At the heart of green tea’s therapeutic power are its catechins, a class of flavonoids and potent antioxidants. The superstar among these is Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG), which often accounts for over half of green tea’s total catechin content. Other notable catechins include epigallocatechin (EGC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), and epicatechin (EC). These compounds are the bodyguards of our cells, tirelessly scavenging free radicals – unstable molecules that cause oxidative stress, a primary driver of aging and disease. EGCG, in particular, possesses a unique molecular structure that allows it to interact with a vast array of cellular pathways, making it a multifaceted agent of health.
But green tea’s symphony of benefits isn’t played by catechins alone. It also contains:
- L-theanine: An amino acid unique to tea, known for inducing a state of calm alertness, enhancing focus without the jitters often associated with caffeine.
- Caffeine: Though generally lower than in coffee, it contributes to green tea’s stimulating effects, improving cognitive function and energy levels.
- Other Flavonoids: Quercetin, kaempferol, and myricetin add to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory arsenal.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Including Vitamin C, B vitamins, folate, potassium, and fluoride.
The magic truly happens in the synergy of these components. It’s not just the presence of EGCG, but its interplay with L-theanine, caffeine, and other compounds that amplifies its effects, creating a holistic impact that is greater than the sum of its parts. This complex interplay is what allows green tea to offer a spectrum of benefits, beginning where our bodies first encounter it: the mouth.
Chapter 2: The First Line of Defense – Green Tea’s Guardianship of Oral Health
Our mouth is the gateway to our body, a bustling microcosm of bacteria, enzymes, and tissues that reflect our overall health. It’s here that green tea begins its protective work, offering a surprisingly robust suite of benefits that extend far beyond simply freshening breath. For centuries, traditional wisdom intuitively recognized tea’s cleansing properties; modern science now illuminates the precise mechanisms.
Battling Bad Breath (Halitosis): One of the most common oral concerns, halitosis, is often caused by volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) produced by bacteria in the mouth. Green tea catechins are remarkably effective at neutralizing these sulfur compounds. Studies have shown that gargling with green tea or simply drinking it can significantly reduce bad breath, often outperforming mints or chewing gum by directly addressing the root cause rather than just masking the odor. The polyphenols bind to the VSCs, rendering them inert, and also inhibit the growth of the odor-producing bacteria.
Fending Off Cavities (Dental Caries): The primary culprit behind cavities is Streptococcus mutans, a bacterium that ferments sugars and produces acids that erode tooth enamel. Green tea catechins act as powerful antimicrobials against S. mutans, inhibiting its growth and its ability to adhere to tooth surfaces and form plaque. Furthermore, catechins can modulate the activity of glucosyltransferases, enzymes crucial for S. mutans to synthesize sticky glucans that form the matrix of plaque. By disrupting this process, green tea helps maintain a healthier oral microbiome and reduces the acidic attacks on our teeth.
Combating Gum Disease (Gingivitis and Periodontitis): Gum disease, ranging from the mild inflammation of gingivitis to the more severe bone-destroying periodontitis, affects a vast percentage of the adult population. Green tea’s anti-inflammatory properties are particularly beneficial here. EGCG and other catechins suppress the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes (like matrix metalloproteinases, MMPs) that contribute to the destruction of gum tissue and bone. Regular consumption of green tea has been associated with a reduction in gum bleeding, pocket depth, and overall inflammation, helping to maintain the integrity of the periodontium and prevent tooth loss. Its antimicrobial action also reduces the overall bacterial load in the mouth, further mitigating the inflammatory response.
A Shield Against Oral Cancer: Beyond everyday oral hygiene, green tea offers a more profound protective layer against oral cancers. The antioxidant properties of catechins help neutralize free radicals and carcinogens that can damage DNA in oral cells, preventing the initiation of cancerous mutations. Furthermore, EGCG has demonstrated an ability to induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in oral cancer cells while leaving healthy cells unharmed. It can also inhibit angiogenesis – the formation of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow and spread – and suppress cellular proliferation. This multi-pronged attack makes green tea a promising natural agent in the chemoprevention of oral cancers, especially in individuals at higher risk.
Through these mechanisms, green tea transforms from a simple beverage into a sophisticated oral health guardian, setting the stage for its wider systemic benefits.
Chapter 3: Beyond the Gums – Safeguarding the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Core
As green tea journeys past the oral cavity, its protective influence expands, reaching the heart of our physiological well-being: the cardiovascular and metabolic systems. These intricate networks dictate our energy, circulation, and the efficiency with which our bodies process nutrients, making their health paramount for longevity and quality of life. Green tea steps in as a profound regulator, its compounds orchestrating a symphony of beneficial changes.
A Heart’s Best Ally: Cholesterol and Blood Pressure Management: Cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Green tea offers multiple pathways to bolster heart health. Its catechins, particularly EGCG, have been shown to help regulate cholesterol levels. They can inhibit the absorption of dietary fats and cholesterol in the gut, reducing the amount that enters the bloodstream. Furthermore, EGCG can modulate the activity of enzymes involved in cholesterol synthesis in the liver, leading to lower levels of "bad" low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, while often preserving or even increasing "good" high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.
Beyond cholesterol, green tea contributes to blood pressure regulation. Its compounds enhance endothelial function, the health of the inner lining of blood vessels. Healthy endothelium produces nitric oxide, a crucial molecule that signals blood vessels to relax and widen, thus lowering blood pressure. The antioxidant properties of green tea also protect LDL cholesterol from oxidation, a critical step in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques – the hardened deposits that narrow arteries and lead to heart attacks and strokes. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, green tea helps maintain the elasticity and patency of blood vessels.
Balancing Blood Sugar: A Defense Against Type 2 Diabetes: The global epidemic of Type 2 Diabetes underscores the urgent need for effective preventive strategies. Green tea offers a compelling natural intervention. Research suggests that catechins can improve insulin sensitivity, meaning the body’s cells become more responsive to insulin, allowing for more efficient glucose uptake from the blood. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduces the burden on the pancreas.
Green tea also influences glucose metabolism by inhibiting enzymes like alpha-glucosidase, which are responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars. By slowing this process, it reduces the post-meal spike in blood glucose. Furthermore, its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects protect pancreatic beta cells, which produce insulin, from damage, preserving their function over time. Regular consumption has been linked to a reduced risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes, making it a valuable dietary component for metabolic health.
Nudging the Scale: Weight Management Support: For those navigating the complexities of weight management, green tea offers a gentle yet effective ally. The combination of caffeine and EGCG creates a synergistic effect that promotes thermogenesis (heat production) and fat oxidation, essentially encouraging the body to burn more calories and fat for energy. EGCG has been shown to inhibit an enzyme called catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), which degrades norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that signals the body to burn fat. By slowing this breakdown, green tea effectively extends the fat-burning effects of norepinephrine.
Additionally, green tea may contribute to appetite control and a reduction in fat absorption, although these effects are typically modest and require consistent consumption alongside a healthy diet and lifestyle. It’s not a magic bullet, but a supportive player in the broader strategy of maintaining a healthy weight.
By fortifying the cardiovascular system and fine-tuning metabolic processes, green tea helps lay a robust foundation for overall health, ensuring that the body’s essential engines run smoothly and efficiently.
Chapter 4: The Brain’s Best Friend – Nurturing Cognitive Function and Neuroprotection
The human brain, an intricate marvel of consciousness and cognition, requires constant nourishment and protection. As we navigate the complexities of modern life, maintaining mental acuity and safeguarding against neurodegenerative diseases becomes increasingly vital. Here too, green tea emerges as a powerful ally, its compounds crossing the blood-brain barrier to offer profound benefits for both immediate cognitive function and long-term neurological health.
The Zen of Focus: Alertness Without the Jitters: One of green tea’s most celebrated qualities is its unique ability to induce a state of "calm alertness." This remarkable effect is primarily due to the synergistic interaction between its caffeine content and the amino acid L-theanine. While caffeine alone can sometimes lead to jitters or anxiety, L-theanine acts as a counterbalance. It directly influences brain activity by increasing alpha wave production, which is associated with a relaxed, focused state, similar to that achieved during meditation.
L-theanine also plays a role in modulating neurotransmitters, boosting levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which has calming effects, and dopamine and serotonin, which regulate mood and cognition. The result is improved attention, memory, and problem-solving abilities, alongside a reduction in stress and anxiety. This makes green tea an ideal beverage for focused work, study, or any activity requiring sustained mental clarity without the overstimulation often associated with coffee.
A Shield Against Cognitive Decline: Neurodegenerative Diseases: The specter of neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases looms large as populations age. Green tea’s neuroprotective properties offer a glimmer of hope in this challenging landscape. Its potent antioxidants, particularly EGCG, are crucial here. The brain is highly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its high metabolic rate and lipid content. EGCG effectively neutralizes free radicals, preventing cellular damage that contributes to neuronal death and cognitive impairment.
Specifically for Alzheimer’s Disease, EGCG has been shown to inhibit the formation of amyloid-beta plaques, the toxic protein aggregates that are a hallmark of the disease. It can also help clear existing plaques and protect neurons from their damaging effects. Furthermore, green tea catechins reduce neuroinflammation, another key factor in the progression of Alzheimer’s.
In the context of Parkinson’s Disease, EGCG demonstrates a protective effect on dopaminergic neurons, the cells that degenerate in this condition, leading to motor symptoms. It helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the substantia nigra, the brain region affected by Parkinson’s, and may interfere with the aggregation of alpha-synuclein, another protein implicated in the disease.
Beyond these specific conditions, green tea’s general ability to improve cerebral blood flow, reduce inflammation, and protect against oxidative damage contributes to overall brain health, potentially slowing age-related cognitive decline and preserving neurological function well into old age. By nourishing the brain and safeguarding its delicate architecture, green tea empowers us to think clearer, remember more, and maintain our mental vitality.
Chapter 5: The Body’s Shield – Fortifying the Immune System and Taming Inflammation
The body’s immune system is its ultimate defense network, a complex army of cells and molecules constantly working to protect us from pathogens, toxins, and internal threats. Inflammation, while a necessary acute response to injury, becomes detrimental when chronic, contributing to a vast array of diseases. Green tea, with its rich bioactive compounds, acts as a sophisticated modulator, strengthening our defenses and quelling the fires of inflammation.
Orchestrating Immune Harmony: Green tea catechins, particularly EGCG, are not merely immune boosters; they are immune modulators. This means they don’t just indiscriminately ramp up immune activity, but rather help to balance and fine-tune its responses, which is crucial for preventing both under-active and over-active (autoimmune) conditions.
Studies have shown that green tea can enhance the function of T-cells, a type of white blood cell central to cell-mediated immunity, helping them to more effectively identify and destroy infected cells or cancer cells. It also supports the activity of gamma-delta T-cells, a less common but highly potent immune cell that acts as a first responder to infection and has anti-tumor properties. Furthermore, green tea’s antioxidants protect immune cells from oxidative damage, ensuring their optimal function.
Quelling the Flames of Chronic Inflammation: Chronic, low-grade inflammation is now recognized as a root cause or exacerbating factor for nearly every major chronic disease, from heart disease and diabetes to autoimmune conditions and cancer. Green tea’s anti-inflammatory power is one of its most profound benefits. EGCG is a master inhibitor of various pro-inflammatory pathways and signaling molecules within the body.
It can suppress the activation of Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a central regulator of inflammatory gene expression. By inhibiting NF-κB, EGCG effectively turns down the production of numerous inflammatory cytokines (like TNF-alpha, IL-6) and enzymes (like COX-2, which is targeted by NSAIDs). This broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory action has significant implications for conditions characterized by chronic inflammation.
For instance, green tea has shown promise in managing symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease driven by chronic joint inflammation. EGCG can protect cartilage from degradation and reduce the inflammation that damages joints. Similarly, for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, green tea’s anti-inflammatory effects can help soothe the inflamed gut lining, though more research is needed to establish its clinical role.
Green tea also has a role in mitigating allergies. Some research suggests that EGCG may inhibit the release of histamine, the compound responsible for many allergic reactions, by stabilizing mast cells. While not a cure, it could potentially reduce the severity of allergic responses.
By bolstering the immune system’s intelligent responses and providing a powerful natural antidote to chronic inflammation, green tea acts as a fundamental shield, protecting the body’s integrity and promoting a state of internal balance and resilience against a myriad of health challenges.
Chapter 6: The Ultimate Defense – Green Tea’s Role in Cancer Prevention and Adjuvant Therapy
Among green tea’s myriad benefits, its potential role in cancer prevention and as an adjuvant therapy stands as perhaps the most compelling and extensively researched. Cancer, a complex disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, is a formidable adversary. Yet, green tea, with its unique cocktail of catechins, offers a multi-pronged defensive strategy, intervening at various stages of carcinogenesis – from initiation to progression and metastasis. This is where the story of green tea’s protective power reaches its most profound chapter.
A Multi-Targeted Anti-Cancer Arsenal: The remarkable efficacy of green tea against cancer lies in its ability to influence multiple cellular pathways simultaneously. This pleiotropic action makes it a broad-spectrum chemopreventive agent, not targeting a single weakness, but rather dismantling the very mechanisms by which cancer takes hold and flourishes.
Key mechanisms include:
- Potent Antioxidant Activity: Cancer often begins with DNA damage caused by free radicals and oxidative stress. EGCG, a formidable antioxidant, neutralizes these reactive oxygen species, preventing mutations and protecting the integrity of our genetic material. It acts as a guardian, preventing the spark that ignites cancer.
- Anti-Proliferative Effects: Cancer cells are defined by their uncontrolled proliferation. Green tea catechins can inhibit the growth of cancer cells by interfering with various signaling pathways that drive cell division. They can arrest the cell cycle, effectively putting a brake on cancerous expansion.
- Induction of Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death): Unlike healthy cells, cancer cells often evade apoptosis, allowing them to live indefinitely. EGCG has a remarkable ability to selectively induce apoptosis in a wide range of cancer cells, forcing them to self-destruct while leaving healthy cells unharmed. This is a critical mechanism for eliminating nascent tumors.
- Anti-Angiogenesis: Tumors, as they grow, require a dedicated blood supply to receive nutrients and oxygen. This process, called angiogenesis, is crucial for tumor growth and metastasis. Green tea catechins can inhibit the formation of new blood vessels, essentially starving the tumor and preventing its expansion and spread.
- Inhibition of Metastasis: The spread of cancer from its primary site to distant parts of the body (metastasis) is what makes cancer so deadly. Green tea compounds have been shown to reduce the invasiveness and migratory capacity of cancer cells, making it harder for them to break away, enter the bloodstream, and colonize new organs.
- DNA Repair Enhancement: Beyond preventing damage, green tea may also enhance the body’s natural DNA repair mechanisms, further safeguarding against the accumulation of mutations that can lead to cancer.
- Epigenetic Modulation: Emerging research indicates that EGCG can influence gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence. It can reactivate tumor suppressor genes that have been silenced in cancer cells and silence oncogenes (cancer-promoting genes), effectively reprogramming cancer cells towards a healthier state.
Targeting Specific Cancers: While research is ongoing, green tea has shown promise across a spectrum of cancers:
- Oral Cancer: Reaffirms its early protective role, with deeper mechanisms now understood at a cellular level.
- Skin Cancer: Both topical and internal consumption of green tea catechins can protect against UV-induced skin damage, reduce inflammation, and inhibit the development of non-melanoma skin cancers. EGCG has also shown potential against melanoma cells.
- Lung Cancer: Studies suggest a reduced risk of lung cancer, particularly in smokers, as green tea can neutralize carcinogens in tobacco smoke and protect lung cells from damage.
- Breast Cancer: EGCG can modulate estrogen pathways, inhibit aromatase (an enzyme that produces estrogen, relevant in some breast cancers), and induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Epidemiological studies have shown lower recurrence rates in green tea drinkers.
- Prostate Cancer: Green tea catechins have been shown to reduce prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels and inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells, suggesting a role in both prevention and management of early-stage disease.
- Colorectal Cancer: Catechins can reduce the formation of polyps (pre-cancerous growths) and inhibit the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells.
- Liver Cancer: Green tea protects liver cells from damage and may reduce the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, especially in individuals with chronic liver diseases.
- Leukemia: EGCG has demonstrated the ability to induce apoptosis in certain leukemia cell lines.
Adjuvant Therapy: Enhancing Conventional Treatments: Beyond prevention, green tea is being explored for its potential to complement conventional cancer treatments. Some studies suggest that EGCG can enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, potentially making cancer cells more susceptible to treatment while simultaneously reducing the side effects on healthy cells. For instance, it may mitigate treatment-induced inflammation and oxidative stress.
It is crucial, however, to emphasize that green tea is not a standalone cure for cancer. Its use in conjunction with conventional therapies must always be discussed with and supervised by an oncologist, as interactions with certain medications are possible.
In its profound ability to intercept, dismantle, and even reprogram cancer cells, green tea offers a powerful and accessible tool in the global fight against this devastating disease, embodying the ultimate defense nature can provide.
Chapter 7: Practical Wisdom – Brewing the Benefits into Daily Life
Having journeyed through the intricate science of green tea’s benefits, the final chapter brings us back to the simplicity of the leaf itself – how to harness its power effectively in our daily lives. The true magic of green tea lies not just in its compounds, but in the ritual of its consumption, transforming a moment of pause into an act of profound self-care.
Choosing Your Green Tea:
The quality of green tea significantly impacts its health benefits.
- Loose Leaf vs. Bags: Loose leaf teas generally offer a superior experience and higher concentration of beneficial compounds, as they allow the leaves to fully unfurl and release their essence. Tea bags, especially those with fannings (dust and small pieces), may contain fewer catechins.
- Origin and Type: Japanese green teas (Sencha, Matcha, Gyokuro) are typically steamed, preserving more EGCG. Chinese green teas (Longjing, Bi Luo Chun) are often pan-fired, resulting in a slightly different flavor profile and catechin balance. Matcha, a powdered green tea, is particularly potent as you consume the entire leaf, making it exceptionally rich in EGCG and L-theanine.
- Organic: Opting for organic varieties minimizes exposure to pesticides, ensuring a purer brew.
The Art of Brewing for Optimal Benefit:
Brewing green tea correctly is essential to extract its full spectrum of compounds without bitterness.
- Water Temperature: Unlike black tea, green tea is delicate. Boiling water will scorch the leaves, releasing harsh tannins and destroying some catechins. Aim for water between 160-180°F (70-80°C). If you don’t have a temperature-controlled kettle, let boiling water sit for 2-3 minutes before pouring.
- Steeping Time: Generally, 2-3 minutes is sufficient. Longer steeping times (beyond 5 minutes) can increase catechin extraction but may also result in a bitter taste. Experiment to find your preference.
- Amount: Use about one teaspoon of loose leaf tea per 8 ounces (240ml) of water, or as directed by the specific tea type.
Optimal Consumption:
- Frequency: For maximum benefits, aim for 2-3 cups of green tea per day. Consistency is key to accumulating its protective effects.
- Timing: Avoid drinking green tea on an empty stomach, especially if you’re sensitive to caffeine, as it can sometimes cause stomach upset. Drinking it between meals is often recommended.
- With or Without Food: While green tea can be enjoyed with food, be mindful of its impact on iron absorption. Catechins can bind to non-heme iron (iron from plant sources), reducing its bioavailability. If you’re at risk of iron deficiency, consume green tea at least an hour before or after iron-rich meals. Adding a squeeze of lemon (Vitamin C) to your tea can counteract this effect and actually enhance catechin absorption.
Important Considerations and Cautions:
- Caffeine Sensitivity: Green tea contains caffeine. While L-theanine buffers its effects, individuals highly sensitive to caffeine should opt for decaffeinated green tea or consume it earlier in the day to avoid sleep disruption.
- Medication Interactions: Green tea, particularly in concentrated extract form, can interact with certain medications. It may interfere with blood thinners like warfarin (due to Vitamin K content, though typically low in tea), some heart medications, and chemotherapy drugs. Always consult your doctor before significantly increasing green tea intake or taking green tea supplements, especially if you are on medication or have underlying health conditions.
- Supplements vs. Tea: Green tea extracts offer concentrated doses of catechins. While potentially more potent, they also carry a higher risk of side effects, especially liver toxicity, if taken in excessive amounts. The whole food matrix of brewed tea is generally safer and provides a more balanced profile of compounds. Stick to brewed tea for daily benefits unless medically advised otherwise.
By integrating green tea into your daily routine with mindful preparation and an understanding of its nuances, you embrace an ancient wisdom that continues to offer profound and wide-ranging health benefits in our modern world.
Conclusion: A Timeless Elixir, Reimagined
Our journey through the full spectrum of green tea’s benefits reveals a narrative far richer and more intricate than merely a comforting beverage. From its ancient origins as a revered medicinal tonic to its modern validation by rigorous scientific inquiry, green tea stands as a powerful testament to nature’s profound capacity for healing and protection.
We have explored its role as a vigilant guardian of oral health, meticulously battling bacteria and inflammation in our mouths. We have seen it transform into a steadfast ally for cardiovascular and metabolic well-being, diligently managing cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood sugar, while subtly supporting weight management. We’ve discovered its profound impact on the brain, nurturing cognitive function with calm focus and standing as a formidable shield against the ravages of neurodegenerative diseases. Its modulating influence on the immune system and its potent anti-inflammatory properties highlight its role as a fundamental fortifier of our body’s internal defenses.
And finally, we delved into its most celebrated and complex benefit: its multi-pronged, sophisticated strategy against cancer, intervening at every stage from prevention to potentially enhancing conventional therapies.
Green tea is more than just a drink; it is a holistic wellness tool, a symbol of balance, and a daily ritual that connects us to both ancestral wisdom and cutting-edge science. Its bioactive compounds, working in elegant synergy, offer a comprehensive approach to health, inviting us to partake in a tradition that promises not just longevity, but vitality.
As you raise your next cup of emerald elixir, remember the intricate journey within each leaf. It is a reminder that sometimes, the most profound health benefits are found in the simplest, most enduring gifts of nature, waiting to be rediscovered, understood, and integrated into a life of well-being. The story of green tea is ongoing, ever unfolding, and perpetually inviting us to sip from its wellspring of health.