Battling Belly Fat: How Avocados Can Aid in Weight Management – A Verdant Chronicle
The Ubiquitous Challenge: Decoding the Belly Fat Enigma
In the sprawling saga of human health, few antagonists are as universally recognized, yet persistently misunderstood, as belly fat. It’s the stubborn bulge that defies countless crunches, the silent saboteur of metabolic harmony, and often, the most visible marker of an internal struggle. More than just an aesthetic concern, the fat that accumulates around our midsection, particularly the deep visceral fat enveloping vital organs, is a harbinger of metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, inflammation, and an increased risk of chronic diseases. For many, the quest to diminish this abdominal adversary feels like an endless battle, fraught with restrictive diets and often, diminishing returns.
But what if the key to turning the tide in this battle lay not in deprivation, but in thoughtful indulgence? What if a creamy, verdant fruit, once maligned for its fat content, held an arsenal of compounds perfectly poised to aid in this very fight? This is the story of the avocado – a tale of ancient lineage, scientific discovery, and its profound potential to become a powerful ally in the intricate dance of weight management, particularly in the stubborn realm of belly fat.
Our journey begins not with a magic pill, but with a deep dive into the science, stripping away myths and revealing the sophisticated mechanisms by which this extraordinary fruit can transform our approach to health, one creamy bite at a time. The audience for this chronicle is not the novice, but the knowledgeable seeker – those who appreciate the nuance of biochemical pathways, the elegance of nutritional synergy, and the power of food as medicine.
The Belly Fat Battleground: Understanding the Enemy Within
Before we introduce our green hero, it’s crucial to intimately understand the foe. "Belly fat" is a colloquial term that encompasses two primary types of adipose tissue:
- Subcutaneous Fat: This is the fat you can pinch just beneath the skin. While excess subcutaneous fat can be aesthetically undesirable, it is generally considered less metabolically dangerous than its deeper counterpart.
- Visceral Fat: This is the insidious fat that lies deep within the abdominal cavity, surrounding organs like the liver, pancreas, and intestines. Visceral fat is metabolically active, secreting hormones and inflammatory compounds (adipokines) that can profoundly disrupt physiological processes.
Why is Visceral Fat the Greater Threat?
The danger of visceral fat stems from its unique metabolic profile. It’s not just a passive storage site; it’s an endocrine organ actively participating in systemic inflammation and hormonal dysregulation.
- Insulin Resistance: Visceral fat releases free fatty acids directly into the portal vein, which carries them to the liver. This can lead to hepatic insulin resistance, where the liver becomes less responsive to insulin, increasing glucose production and contributing to higher blood sugar levels. This, in turn, can perpetuate a vicious cycle of fat storage, especially around the midsection.
- Inflammation: Visceral adipocytes produce pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha, IL-6, and CRP. Chronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of obesity and is implicated in numerous chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Beyond inflammatory markers, visceral fat can disrupt the balance of other hormones, including cortisol (stress hormone), leptin (satiety hormone), and adiponectin (an anti-inflammatory hormone that improves insulin sensitivity). An imbalance in these can lead to increased appetite, reduced energy expenditure, and further fat accumulation.
The battle against belly fat, therefore, is not merely about calorie restriction, but about addressing these underlying metabolic and inflammatory pathways. And this is where the avocado steps onto the stage.
The Avocado’s Ancient Lineage and Modern Resurgence: From Alligator Pear to Superfood Status
Our story truly begins thousands of years ago in Mesoamerica, where the avocado, or ahuacatl as it was known by the Aztecs, was revered as a symbol of fertility and a vital food source. For centuries, this fruit, often called the "alligator pear" due to its rough, green skin, remained largely confined to its native lands.
Its journey to global recognition has been a winding one, marked by periods of skepticism. For much of the 20th century, as the "low-fat" dogma swept across the Western world, the avocado, with its rich, creamy texture and high-fat content, was viewed with suspicion. It was seen as an indulgence, a calorie bomb to be avoided by anyone serious about weight management.
However, as nutritional science matured, and our understanding of fats evolved, the narrative began to shift dramatically. Researchers uncovered the distinct benefits of different types of fats, distinguishing between harmful trans fats, often problematic saturated fats, and the profoundly beneficial unsaturated fats. The avocado, brimming with the latter, emerged from the shadows of dietary dogma to claim its rightful place as a nutritional powerhouse – a superfood celebrated not just for its unique flavor and versatility, but for its profound health benefits.
This resurgence wasn’t a mere culinary trend; it was a scientific vindication, setting the stage for its role in our fight against belly fat.
The Avocado’s Arsenal: A Deep Dive into its Nutritional Powerhouse
To understand how avocados aid in weight management, especially against visceral fat, we must first dissect its remarkable composition. It’s a symphony of compounds, each playing a crucial role.
A. The Mighty MUFAs: Monounsaturated Fats – The Heart of the Matter
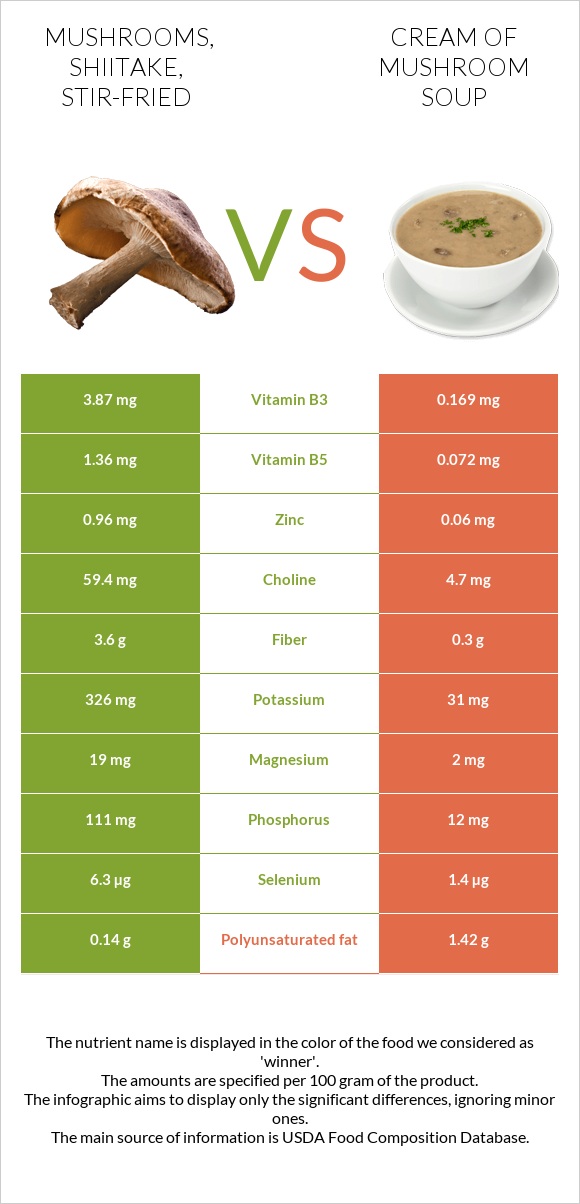
The most prominent feature of the avocado’s nutritional profile is its fat content, predominantly monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), with oleic acid being the star player. Far from being detrimental, these healthy fats are cornerstones of a balanced diet and crucial for metabolic health.
- Satiety and Reduced Cravings: MUFAs are digested more slowly than carbohydrates, leading to a prolonged feeling of fullness. This enhanced satiety helps to reduce overall calorie intake by curbing mindless snacking and preventing overeating at subsequent meals. When you feel satisfied, your brain doesn’t trigger the incessant hunger signals that often lead to poor food choices.
- Metabolic Flexibility: Research suggests that MUFAs can improve the body’s ability to burn fat for energy, rather than relying solely on carbohydrates. This metabolic flexibility is critical for weight loss and preventing fat accumulation.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Oleic acid, the primary MUFA in avocados, has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity. By making cells more responsive to insulin, avocados help the body efficiently utilize glucose, preventing spikes in blood sugar and reducing the likelihood of fat storage, particularly visceral fat, which is strongly linked to insulin resistance.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: MUFAs possess potent anti-inflammatory effects. As we’ve established, chronic low-grade inflammation is a key driver of visceral fat accumulation and metabolic dysfunction. By dampening inflammatory pathways, avocados contribute to a healthier metabolic environment.
Contrast this with the effects of refined carbohydrates or unhealthy saturated/trans fats, which can trigger insulin spikes, promote inflammation, and encourage fat storage. The avocado’s fat content is not merely "good"; it’s strategically advantageous.
B. Fiber: The Unsung Hero of Gut Health and Satiety
While fats often steal the spotlight, the avocado’s fiber content is equally, if not more, critical for weight management. A single medium avocado contains approximately 10-13 grams of fiber, providing a significant portion of the recommended daily intake. This fiber comes in two crucial forms:
- Soluble Fiber: This type of fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance in the digestive tract. It slows down digestion, further enhancing satiety and prolonging the feeling of fullness. Critically, soluble fiber helps to stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of glucose, directly impacting insulin response and reducing the propensity for belly fat storage.
- Insoluble Fiber: This fiber adds bulk to stool and aids in digestive regularity, promoting a healthy gut environment.
The Gut-Belly Fat Connection: The role of fiber extends beyond mere digestion. It acts as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in your gut microbiome. A thriving, diverse gut microbiome is increasingly recognized as a cornerstone of metabolic health.
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs): When gut bacteria ferment soluble fiber, they produce SCFAs like butyrate, propionate, and acetate. These SCFAs have profound effects:
- Butyrate: Provides energy to colon cells, strengthens the gut barrier, and reduces gut inflammation.
- Propionate: Can signal satiety to the brain and may play a role in glucose homeostasis.
- Acetate: Can be converted to other SCFAs or used for energy.
- Reduced Endotoxemia: A healthy gut barrier, supported by fiber and SCFAs, prevents the leakage of bacterial toxins (lipopolysaccharides or LPS) into the bloodstream, a condition known as endotoxemia. Endotoxemia is a major trigger for systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and visceral fat accumulation. By promoting gut integrity, avocados indirectly combat belly fat.
In essence, the avocado’s fiber content doesn’t just fill you up; it cultivates an internal ecosystem conducive to leanness and metabolic well-being.
C. Vitamins & Minerals: The Supporting Cast with Leading Roles
Beyond fats and fiber, avocados are packed with an impressive array of micronutrients that contribute to overall health and indirectly support weight management:
- Potassium: Avocados are richer in potassium than bananas. Potassium is vital for fluid balance, nerve signals, and muscle contractions. It also plays a role in blood pressure regulation and can help counteract the effects of sodium, reducing water retention and bloating, which can sometimes be confused with fat.
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting and bone health.
- Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen synthesis.
- Vitamin E: Another potent antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage, reducing inflammation.
- B Vitamins (especially B6 and Folate): Crucial for energy metabolism, converting food into usable energy, and supporting neurological function. Folate is particularly important for cell growth and DNA repair.
While not directly burning fat, these micronutrients ensure optimal bodily function, supporting energy levels, reducing fatigue, and creating a healthier internal environment where weight management efforts can thrive.
D. Phytochemicals & Antioxidants: The Invisible Protectors
Avocados contain a variety of phytochemicals, plant compounds with powerful health benefits, including carotenoids (lutein, zeaxanthin), and polyphenols.
- Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects: These compounds actively scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation throughout the body. Given that chronic inflammation is a key driver of visceral fat and metabolic dysfunction, the avocado’s antioxidant punch is another strategic advantage in the battle against belly fat. Lutein and zeaxanthin, in particular, are well-known for their benefits to eye health, but their systemic antioxidant properties contribute to overall cellular resilience.
The avocado, therefore, is not a one-trick pony. It’s a comprehensive nutritional package, meticulously designed by nature to nourish, protect, and optimize.
Avocados and Weight Management: The Scientific Mechanisms Unveiled
Now that we’ve explored the avocado’s impressive composition, let’s connect the dots to how these elements synergistically contribute to weight management, with a specific focus on battling belly fat.
A. Satiety and Appetite Control: The End to Endless Cravings
The most immediate and tangible benefit of incorporating avocados into your diet is their remarkable ability to induce satiety. The combination of healthy monounsaturated fats and soluble fiber creates a powerful duo that significantly impacts appetite regulation:
- Delayed Gastric Emptying: Fats and fiber slow down the rate at which food leaves the stomach. This prolonged digestion sends continuous signals of fullness to the brain, preventing the rapid return of hunger that often follows meals high in refined carbohydrates.
- Hormonal Regulation: Avocados influence the release of key satiety hormones. Cholecystokinin (CCK) and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) are gut hormones that signal fullness to the brain and reduce appetite. Studies have shown that meals containing avocados can increase the post-meal release of these hormones, leading to greater satisfaction and reduced desire to eat for several hours.
- Reduced Snacking and Calorie Intake: When you feel genuinely full and satisfied, you’re less likely to reach for unhealthy snacks between meals. Research has demonstrated that individuals who consume avocados with a meal report significantly less hunger and a reduced desire to eat compared to those who don’t. Over time, this consistent reduction in overall calorie intake, achieved without feeling deprived, is a sustainable pathway to weight loss.
For those battling belly fat, this sustained satiety is invaluable. It helps break the cycle of overeating driven by constant hunger signals, which often leads to excess calorie consumption and subsequent fat storage.
B. Blood Sugar Regulation and Insulin Sensitivity: Targeting the Root Cause of Belly Fat
Perhaps one of the most critical mechanisms by which avocados combat belly fat is their positive influence on blood sugar and insulin sensitivity. As discussed, insulin resistance is a major driver of visceral fat accumulation.
- Slowed Glucose Absorption: The soluble fiber in avocados forms a gel in the digestive tract, slowing down the absorption of carbohydrates. This prevents rapid spikes in blood glucose levels after a meal.
- Improved Insulin Response: When blood sugar rises slowly, the pancreas releases insulin more steadily and effectively. Over time, this consistent regulation can improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, meaning cells become more responsive to the hormone.
- Reduced Fat Storage: When insulin sensitivity is optimized, the body is better able to utilize glucose for energy rather than storing it as fat. Crucially, improved insulin sensitivity directly correlates with a reduction in visceral fat, as this type of fat is highly responsive to insulin signaling. By stabilizing blood sugar and enhancing insulin function, avocados directly address one of the primary metabolic pathways leading to belly fat.
C. Gut Health: The Second Brain Connection and Metabolic Harmony
The intricate relationship between our gut microbiome and metabolic health is an exploding field of research. Avocados, through their rich fiber content, are powerful modulators of this "second brain."
- Prebiotic Power: The fiber in avocados acts as a prebiotic, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria. A diverse and robust microbiome is associated with a leaner body composition and improved metabolic markers.
- SCFA Production: As beneficial bacteria ferment avocado fiber, they produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). These SCFAs, particularly butyrate, not only fuel gut cells but also influence energy metabolism, enhance insulin sensitivity, and reduce systemic inflammation.
- Reduced Inflammation and Endotoxemia: A healthy gut barrier, strengthened by SCFAs, prevents the leakage of inflammatory bacterial components (LPS) into the bloodstream. This reduction in endotoxemia directly lowers systemic inflammation, which, as we know, is a key contributor to visceral fat accumulation and insulin resistance.
By fostering a healthier gut environment, avocados contribute to a systemic reduction in inflammation and an improvement in metabolic function, creating conditions less favorable for belly fat storage.
D. Nutrient Absorption Enhancement: Maximizing Your Diet’s Potential
While not a direct weight-loss mechanism, the healthy fats in avocados play a vital supporting role: they enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) from other foods eaten concurrently. Many of these vitamins are crucial for metabolic health, immune function, and overall well-being. By ensuring your body can efficiently utilize the nutrients from your entire diet, avocados indirectly support a healthy metabolism and energy levels, which are foundational for sustainable weight management. For example, Vitamin D deficiency is often linked to obesity and metabolic dysfunction, and consuming avocados with vitamin D-rich foods can optimize its absorption.
E. Anti-Inflammatory Power: Dousing the Metabolic Fire
We’ve touched upon inflammation repeatedly because it’s so central to the problem of belly fat. The avocado’s combination of MUFAs, fiber, vitamins (C, E), and phytochemicals (carotenoids, polyphenols) provides a potent anti-inflammatory cocktail.
- Systemic Impact: By reducing chronic low-grade inflammation throughout the body, avocados help to mitigate one of the key drivers of insulin resistance and visceral fat accumulation. When the body is in a state of chronic inflammation, it’s less efficient at burning fat and more prone to storing it, particularly around the midsection.
The avocado’s anti-inflammatory properties don’t just feel good; they actively create a more favorable metabolic environment for fat loss, especially from the visceral stores.
Integrating Avocados into Your Lifestyle: A Practical Guide to Harnessing the Green Gold
Understanding the science is one thing; putting it into practice is another. The beauty of the avocado lies in its versatility. However, a knowledgeable audience understands that even beneficial foods require mindful consumption.
Portion Control and Caloric Density: While incredibly healthy, avocados are calorie-dense due to their fat content. A standard serving size is typically one-third to one-half of a medium avocado. Incorporating this portion into your daily meals can provide significant benefits without excessive calorie intake. The key is to replace less healthy fats or calorie-dense ingredients, rather than simply adding avocado on top of an already high-calorie meal.
Creative Culinary Integration:
- Breakfast Powerhouse: Add slices to whole-grain toast with an egg, blend into a green smoothie for sustained energy, or dice into an omelet for creaminess and satiety.
- Lunchtime Hero: Transform salads into satisfying meals, mash into a vibrant sandwich spread instead of mayonnaise, or create a quick and healthy wrap filling.
- Dinner Delight: Use as a creamy base for sauces (e.g., a dairy-free pasta sauce), top grilled fish or chicken, or incorporate into vibrant bowls with grains and vegetables.
- Snack Savior: A simple half avocado with a sprinkle of salt and pepper is a remarkably satisfying and nutritious snack. Guacamole (made with fresh ingredients) is another excellent option when paired with raw vegetables or whole-grain crackers.
- Unexpected Desserts: Believe it or not, avocados can create surprisingly rich and creamy desserts, like chocolate mousse or dairy-free ice cream, without the need for excessive sugar or unhealthy fats.
Synergy with Other Foods: The fat in avocados isn’t just good for you; it’s a team player. Pair avocados with other nutrient-rich foods, especially those high in fat-soluble vitamins (like leafy greens, carrots, tomatoes), to maximize the absorption of these vital nutrients. A salad with avocado isn’t just tastier; it’s nutritionally superior.
Beyond the Fruit: Avocado Oil: For cooking, particularly at higher temperatures, avocado oil is an excellent choice. With a high smoke point and a similar healthy fat profile to the fruit, it’s a stable and heart-healthy option for sautéing, roasting, and even frying.
Addressing the Nuances and Common Misconceptions: The Holistic Picture
No single food is a magic bullet, and the avocado is no exception. A knowledgeable perspective requires acknowledging these nuances.
- "Too High in Fat/Calories": This misconception has largely been debunked. The type of fat is paramount. As we’ve extensively discussed, the MUFAs in avocados are beneficial, not detrimental, for metabolic health and satiety. When consumed in appropriate portions as part of a balanced diet, avocados contribute to weight management, not weight gain.
- Balance is Key: Avocados are a powerful tool, but they are part of a holistic strategy. Sustainable weight management, particularly the reduction of belly fat, requires a multi-pronged approach: a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, regular physical activity (including strength training), adequate sleep, and stress management. The avocado supports these efforts; it doesn’t replace them.
- Individual Variability: While the mechanisms are scientifically sound, individual responses can vary. Factors like genetics, existing gut microbiome composition, and overall lifestyle can influence how effectively an individual responds to dietary interventions.
- Sustainability: While beyond the scope of direct weight management, a knowledgeable audience is often aware of broader impacts. Responsible sourcing and consumption of avocados, considering their water footprint and ethical farming practices, is a growing consideration.
The Holistic Picture: Beyond the Belly – A Legacy of Wellness
The story of the avocado’s contribution to health extends far beyond the battle against belly fat. Its rich nutrient profile confers a multitude of benefits that reinforce its status as a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle:
- Heart Health: The MUFAs, potassium, and fiber in avocados contribute to improved cholesterol profiles (lowering LDL and increasing HDL), reduced blood pressure, and overall cardiovascular protection.
- Skin Health: Vitamins C and E, along with healthy fats, contribute to skin elasticity, hydration, and protection against oxidative damage.
- Eye Health: Lutein and zeaxanthin are powerful antioxidants concentrated in the eyes, protecting against age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
- Cognitive Function: Healthy fats are essential for brain health, supporting cognitive function and potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Joint Health: The anti-inflammatory compounds can help alleviate symptoms of arthritis and promote overall joint well-being.
By embracing avocados, we’re not just targeting a single problem area; we’re investing in a comprehensive strategy for long-term health and vitality.
Conclusion: The Avocadian Promise – A Strategic Ally in the Wellness Journey
The journey to understand belly fat and the avocado’s role in its management reveals a profound truth: food is not merely fuel; it is information. The avocado, this verdant marvel, communicates messages of satiety, metabolic balance, reduced inflammation, and gut health to our bodies.
We began with the ubiquitous challenge of belly fat, understanding its insidious nature as a metabolic disruptor. We then delved into the avocado’s rich history and its triumphant re-evaluation by modern science. The core of our chronicle lay in dissecting its potent arsenal – the mighty MUFAs, the unsung hero fiber, the crucial supporting cast of vitamins and minerals, and the invisible protectors, the phytochemicals.
Finally, we illuminated the precise scientific mechanisms by which these components synergistically address the very roots of belly fat: enhancing satiety, improving insulin sensitivity, cultivating a healthy gut microbiome, and dousing the fires of chronic inflammation. This is not a story of a magic bullet, but of a strategic ally – a food that, when thoughtfully integrated into a holistic lifestyle, can empower individuals in their quest for sustainable weight management and vibrant health.
The avocado, once a misunderstood fat bomb, stands today as a testament to the evolving wisdom of nutrition science. It is a symbol of how understanding the nuanced power of whole foods can transform our approach to health, making the battle against belly fat not a struggle of deprivation, but a journey of delicious discovery and profound wellness. Embrace the green gold, and let its ancient wisdom guide you towards a healthier, leaner future.